🔸 MEDEC: AI Error Detection Benchmark for Medical Use Cases
How MEDEC is Revolutionizing Medical Error Detection with AI
Welcome back to Neural Notebook! Today, we're diving into the fascinating world of medical error detection with a spotlight on MEDEC, a groundbreaking AI system that's making waves in healthcare.
If you enjoy our content - please subscribe!
🔬 What is MEDEC?
Imagine a tool that can sift through clinical notes and spot errors faster than a caffeine-fueled doctor on a night shift. That's MEDEC, or Medical Error Detection and Correction. It's the first publicly available benchmark designed to assess the ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to identify and correct errors in clinical notes, playing a vital role in patient safety and clinical accuracy.
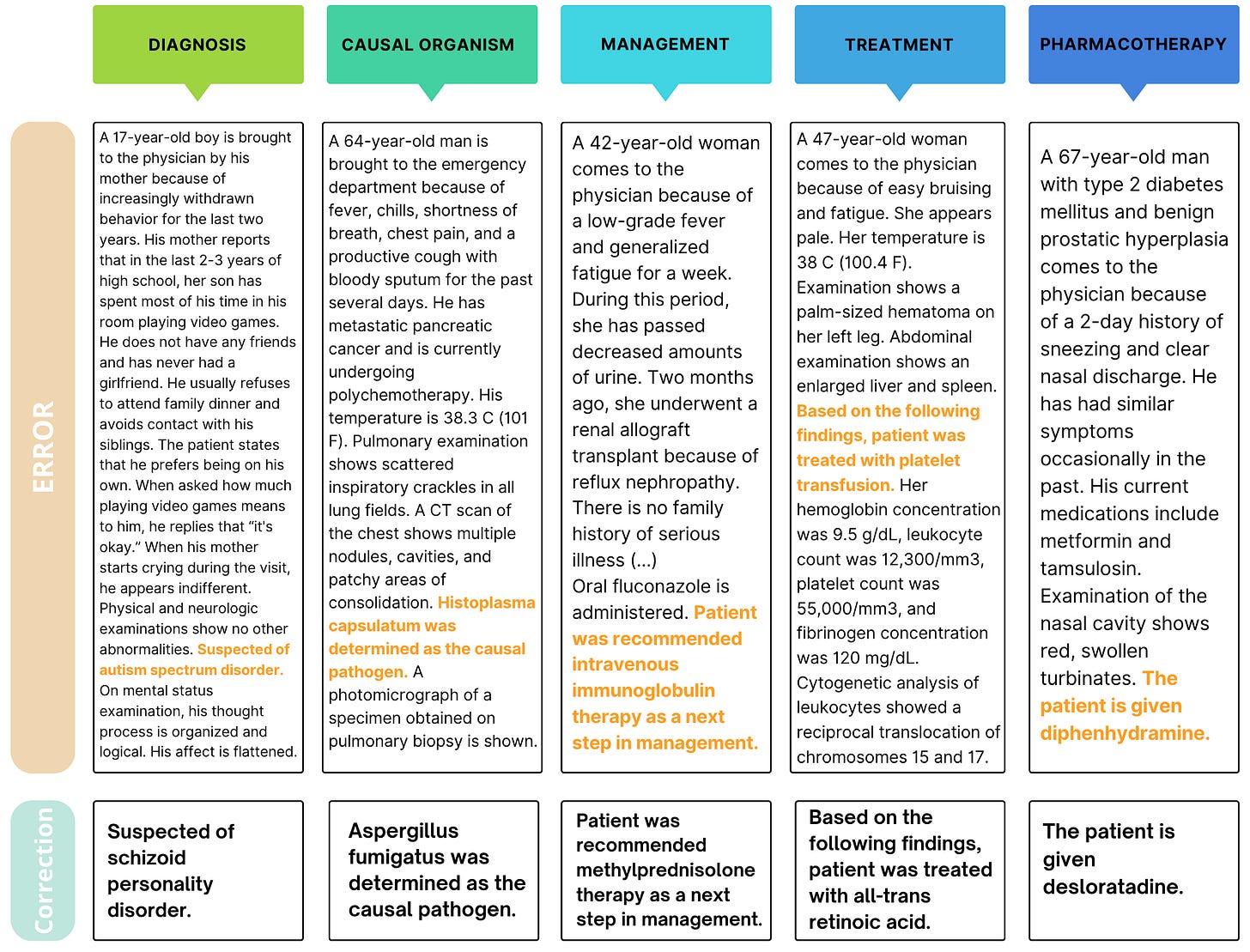
Why is this important? Medical errors can have serious consequences, and MEDEC aims to reduce these by providing a systematic approach to identifying and correcting mistakes in clinical documentation. With a dataset comprising 3,848 clinical texts, including 488 clinical notes from three US hospital systems, MEDEC covers five types of medical errors: Diagnosis, Management, Treatment, Pharmacotherapy, and Causal Organism.
⚙️ How Does MEDEC Work?
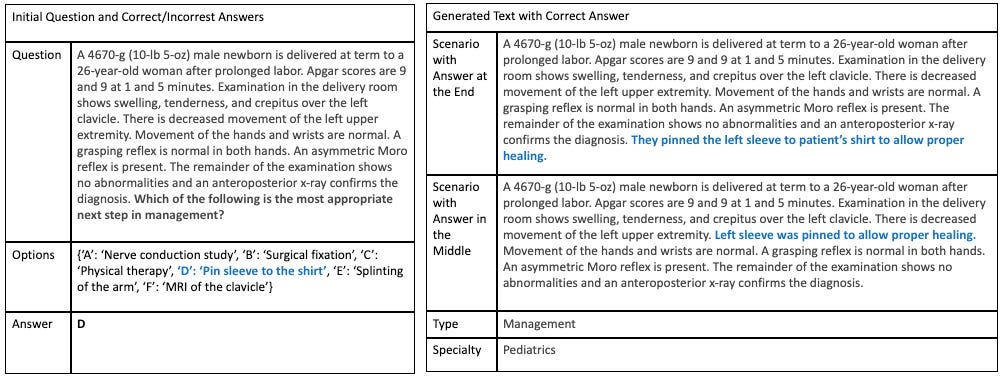
At its core, MEDEC is all about leveraging AI to enhance clinical accuracy. The benchmark involves three subtasks for evaluation: predicting the error flag, extracting the sentence containing the error, and generating a corrected sentence for flagged texts with errors. This structured approach allows for a comprehensive assessment of LLMs' capabilities in medical error detection and correction.
Simply put, MEDEC uses AI to "read" clinical notes and identify potential errors. It then suggests corrections, much like a spellchecker for medical documentation. This process not only improves the accuracy of clinical notes but also helps healthcare providers focus on delivering quality care.
🩻 The Power of AI in Healthcare
MEDEC isn't just about detecting errors—it's about transforming healthcare through AI. By utilizing recent LLMs like GPT-4, Claude 3.5 Sonnet, and Gemini 2.0 Flash, MEDEC evaluates the performance of these models in real-world scenarios. This is crucial for developing automated systems that enhance patient safety and quality of care.
The integration of AI in healthcare is a game-changer, offering the potential to reduce medical errors significantly. With MEDEC, healthcare providers can ensure that clinical notes are accurate and reliable, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
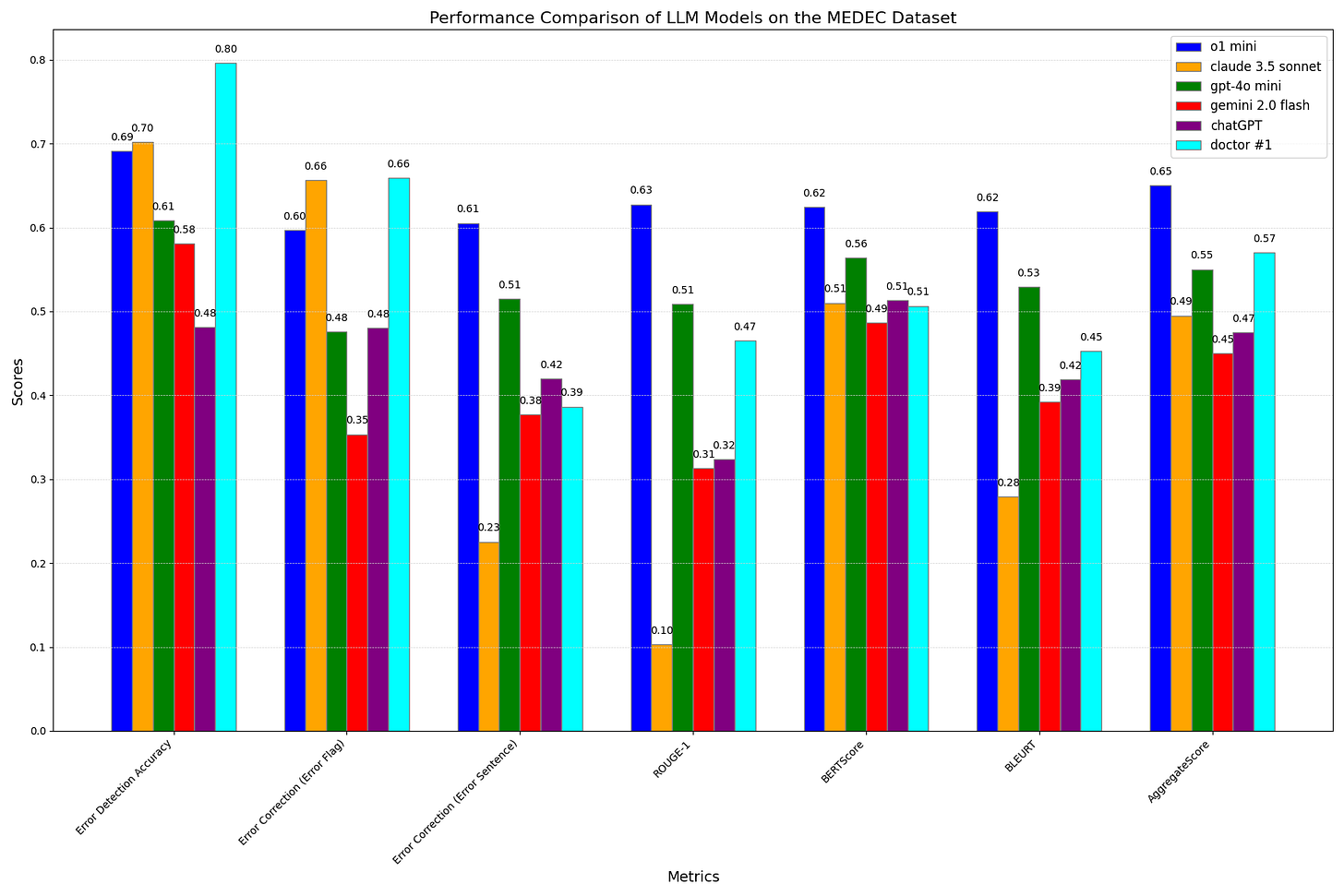
As you can see here, different models perform differently on different benchmarks (i.e. error correction, error detection, etc) and now that we see the deficiencies, researchers can design better models that will pass more of the test cases.
🙊 Challenges and Limitations
Of course, no system is perfect, and MEDEC is no exception. While recent LLMs perform well in error detection and correction, they are still outperformed by medical doctors in these tasks. This highlights the need for continuous improvement and collaboration between AI and human expertise.
Moreover, MEDEC's reliance on historical data means that it may struggle with new or rare medical conditions that aren't well-represented in the dataset. However, ongoing research and development are addressing these challenges, paving the way for more robust and reliable AI systems in healthcare.
🚀 Recent Advancements
The world of AI is ever-evolving, and MEDEC is no different. Researchers have been utilizing prompt engineering techniques to enhance the performance of LLMs in medical error detection and correction. This involves integrating error categorization into prompts to facilitate better reasoning and more accurate results.
Additionally, ensemble methods and self-consistency approaches are being explored to improve the robustness and performance of LLMs. These advancements aim to develop more reliable and interpretable AI systems for clinical documentation analysis.
📚 Learn More about MEDEC
Authored by Asma Ben Abacha, Wen-wai Yim, Yujuan Fu, Zhaoyi Sun, Meliha Yetisgen, Fei Xia, and Thomas Lin, this research is a collaborative effort between Microsoft Health and Life Sciences AI and the University of Washington's Biomedical and Health Informatics department.
To explore the full paper and its contributions, visit the arXiv link.
🔮 Future
Looking ahead, the potential for MEDEC and similar AI-driven systems is vast. With improvements in data collection, AI model optimization, and collaboration between AI and human expertise, the future of medical error detection will likely be more accurate, efficient, and reliable than ever before.
As more healthcare providers adopt AI-based systems, we could see a world where medical errors are significantly reduced, leading to safer and more effective patient care.
The rise of models like MEDEC opens up a variety of opportunities:
Enhanced Clinical Accuracy: By leveraging AI to detect and correct medical errors, healthcare providers can ensure that clinical notes are accurate and reliable, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
Improved Patient Safety: With a systematic approach to identifying and addressing medical errors, MEDEC contributes to enhanced patient safety and healthcare quality.
Collaboration in Research: The integration of AI in healthcare fosters collaboration between researchers, healthcare providers, and AI developers, leading to continuous improvement and innovation.
MEDEC is more than just a benchmark—it's a glimpse into the future of AI-driven healthcare. As we continue to explore the possibilities of AI in medical error detection, the potential for improved patient outcomes and healthcare quality is immense.
Until next time,
The Neural Notebook Team
Twitter | Website
P.S. Don't forget to subscribe for more updates on the latest advancements in AI, and how you can start leveraging them in your own projects.